If you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, you may be wondering what your options are for treating it. Periodontal disease is a serious condition that affects the gums and the bones that support the teeth.
This disease can cause inflammation, bleeding, receding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and tooth loss. Fortunately, there are several treatments available for periodontal disease. Here are some of the most common options.
Scaling and Root Planing
Dental providers employ a non-surgical procedure called scaling and root planing to clean the teeth and the roots below the gum line. Your dentist will use special instruments to remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and smooth the rough surfaces of the roots. The removal helps to eliminate bacteria and toxins that cause inflammation and infection.
Scaling and root planing may take one or more visits to complete, depending on the extent of your periodontal disease. You may experience a bit of discomfort, bleeding, or sensitivity after the procedure, but these should subside within a few days.
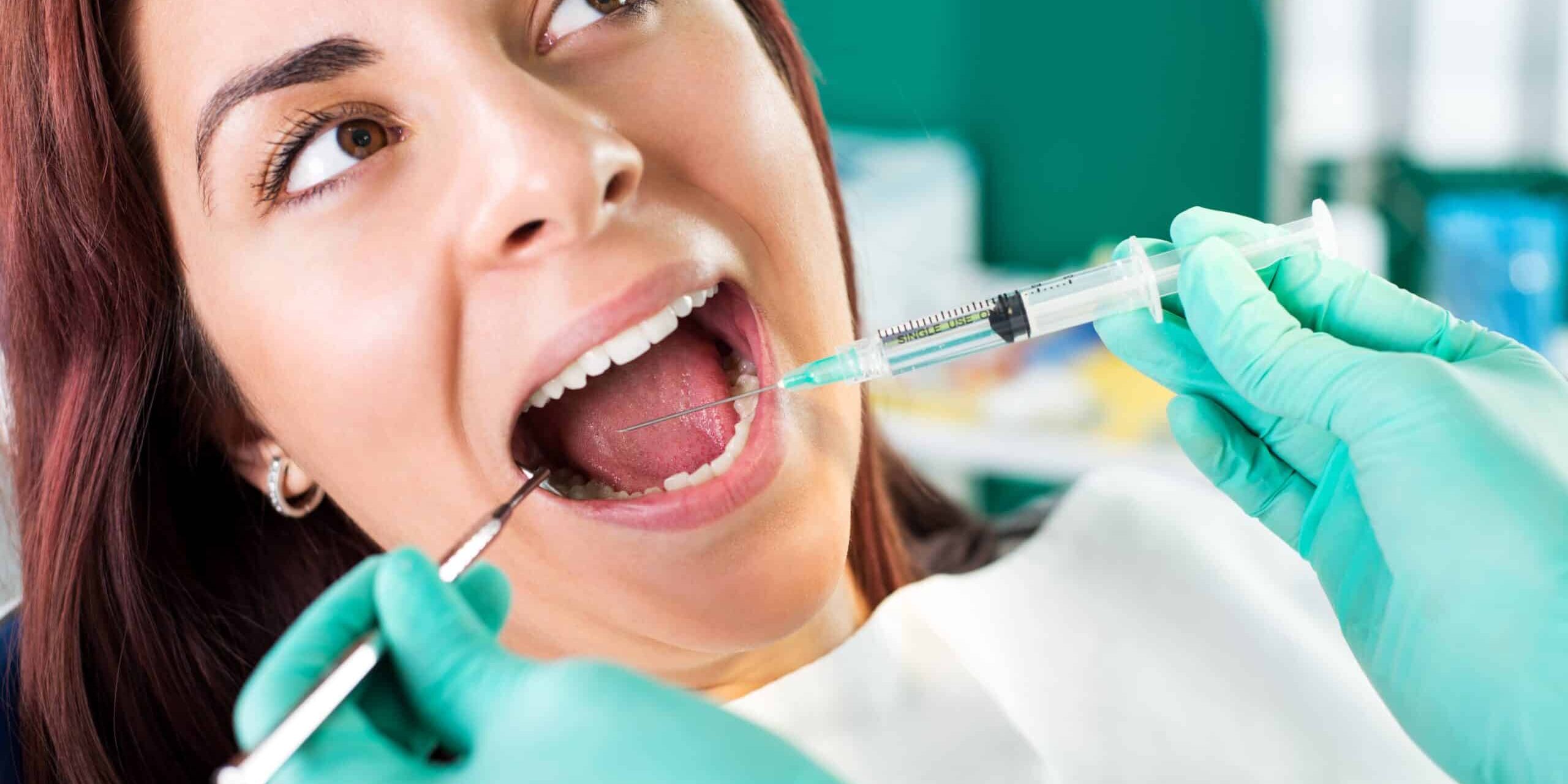
Antibiotics
Sometimes, scaling and root planing alone are not enough to control the infection caused by periodontal disease. In these cases, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help fight the bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Antibiotics can be taken orally or applied directly to the gums via an injectable powder. Usually used in conjunction with scaling and root planing or other treatments, antibiotic medication is not a standalone therapy.
Surgery
If your periodontal disease is severe or does not respond to non-surgical treatments, you may need surgery to restore your oral health. There are different types of surgery that can be performed to treat periodontal disease, such as:
- Flap surgery. Periodontal flap surgery involves lifting the gums back to expose the roots and the bone. The dentist then removes any infected tissue and reshapes the bone to eliminate any defects. The gums are then sutured back in place, creating a tighter fit around the teeth.
- Bone grafting. Bone grafting replaces any lost bone due to periodontal disease with your own bone, synthetic bone, or donated bone. The bone graft helps to stimulate new bone growth and support the teeth.
- Soft tissue grafting. With soft tissue grafting, your provider takes tissue from another part of your mouth or from a donor and attaches it to your gums to cover any exposed roots or fill any gaps between the teeth. This helps to prevent further gum recession and improve the appearance of your smile.
- Guided tissue regeneration (GTR). GTR involves placing a special material between the bone and the gum tissue to prevent the gum from growing into the bone space. This allows the bone and the connective tissue to regenerate and support the teeth.
- Dental implants. If you have lost any teeth due to periodontal disease, you may consider getting dental implants to replace them. Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are surgically inserted into the jawbone. They can support crowns, bridges, or dentures that look and function like natural teeth.
You may experience some pain, swelling, or bleeding after surgery, but these should subside within a few days or weeks. You will also need to follow your post-operative instructions to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Periodontal disease is a serious condition that can affect your oral health and overall well-being. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, you can stop its progression and restore your smile.
If you have symptoms of periodontal disease, such as red, swollen, bleeding, or receding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, or tooth loss, contact Commack Hills Dental Group. The sooner you get treatment, the better your chances of saving your teeth and preventing further damage.